What Is Mail Archiving and Why It Matters
Mail Archive is the process of moving older or less frequently accessed emails from your primary inbox to a separate storage file, usually a PST file. This helps keep your mailbox organized, reduces clutter, and ensures faster performance in Microsoft Outlook. By archiving emails instead of deleting them, you keep all important communication safe while maintaining a clean and efficient mailbox structure.
Benefits of Mail Archiving for Users
Email archiving helps users free up mailbox space, especially when working with limited storage in Outlook or Exchange accounts. It protects important emails by shifting them into a secure archive file, reducing the risk of accidental deletion. Archiving also keeps your inbox clean and helps you manage years of communication without overwhelming your active mailbox. For professionals, archived emails act as a reliable record for work history, client communication, and compliance.
Why Archiving Improves Outlook Performance
A smaller mailbox loads faster and runs more smoothly. Archiving reduces the size of your active inbox, which helps Outlook open quicker, search faster, and sync more efficiently—especially when using Exchange or Office 365 accounts.
When You Should Create an Archive File (PST)
You should create a PST file when your mailbox is nearing storage limits, Outlook becomes slow, or when you want to organize older emails without deleting them. Archiving is ideal for long-term storage and safekeeping of important messages.
Prerequisites Before Starting Mail Archiving
Before you begin the mail archiving process in Outlook, it’s important to ensure that your system and Outlook setup are ready. Meeting these prerequisites will help you avoid errors and ensure a smooth archiving experience.
Outlook Version Requirements
Mail archiving is supported in most modern versions of Microsoft Outlook, including Outlook 2016, 2019, 2021, and Microsoft 365. If you are using an older version like Outlook 2010 or 2013, archiving may still work, but certain features—such as advanced AutoArchive settings or improved PST handling—may be limited. For best results, always keep Outlook updated with the latest patches and improvements. You can check your version by going to File → Office Account → About Outlook.
Available Storage Space Needed
Archiving emails creates a PST file, and this file needs free storage space to save and process email data. Make sure the drive you choose for storing the archive has at least 2–5 GB of free space, depending on the size of your mailbox. If your mailbox is very large, consider archiving by smaller date ranges to prevent PST corruption and ensure faster performance.
Understanding Auto Archive vs Manual Archive
Outlook provides two methods for archiving—Auto Archive and Manual Archive. Auto Archive automatically moves old emails to a PST file based on predefined rules, making it ideal for long-term maintenance. Manual Archive gives you complete control, allowing you to select specific folders, dates, and file locations. For precise and one-time cleanup, Manual Archive is the preferred method.
Step-by-Step Guide to Archive Emails in Outlook
Archiving your emails in Outlook is one of the most effective ways to free up mailbox space, improve application speed, and securely store old messages without deleting them. Follow this clear, step-by-step guide to manually archive your emails in Microsoft Outlook.
1. Access Account Settings

- Open Outlook and click on the File tab at the top-left corner.
- On the Account Information page, click on Account Settings, then select Account Settings again from the dropdown menu.
- In the list of email accounts, double-click on your email account to open the configuration window.
2. Disable Cached Exchange Mode

- In the Exchange Account Settings window, uncheck “Use Cached Exchange Mode to download email to an Outlook data file.”
- After unchecking the option, click Next to proceed and then close the window.
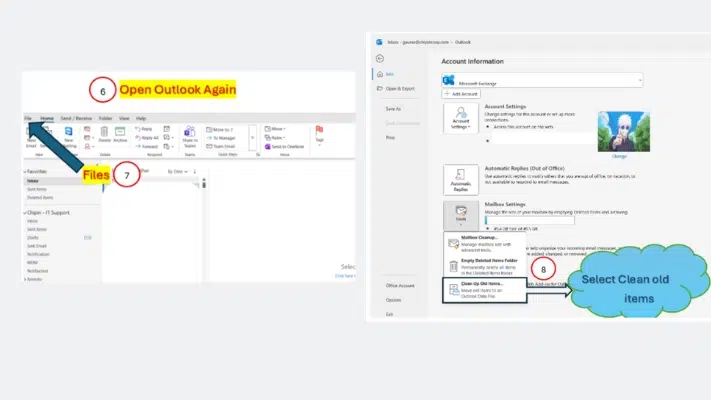
3. Restart Outlook and Access Archive Tools

- Close Outlook completely and open it again.
- After Outlook opens, click on the File tab once more.
- In the Account Information section, click on Mailbox Cleanup and then select Clean Up Old Items to open the manual archiving options.
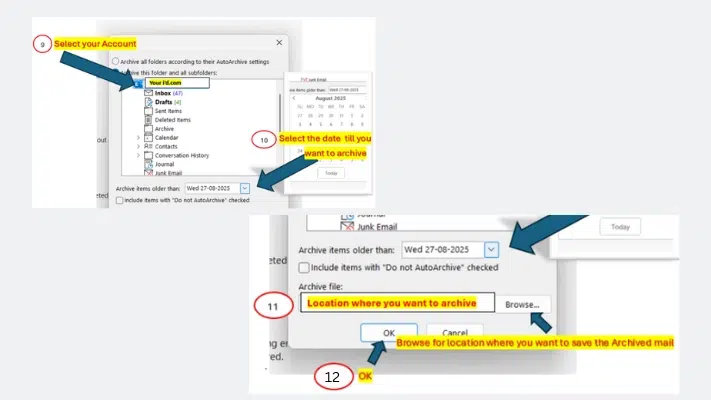
4. Configure Archive Settings

- In the Archive window, select your email account or specific folders you want to archive.
- Choose the date range by selecting the option “Archive items older than” and picking your desired archive date.
- Click Browse to select the location where you want the PST archive file to be stored.
- After choosing the folder and archive location, click OK to start the archiving process.
5. Archiving Process Begins (Archiving Bar)

Outlook will now begin archiving your emails.
A status bar labeled “Archiving…” will appear at the bottom of Outlook.
- Archiving is currently in progress.
- Once the progress bar disappears, your archiving is successfully completed.
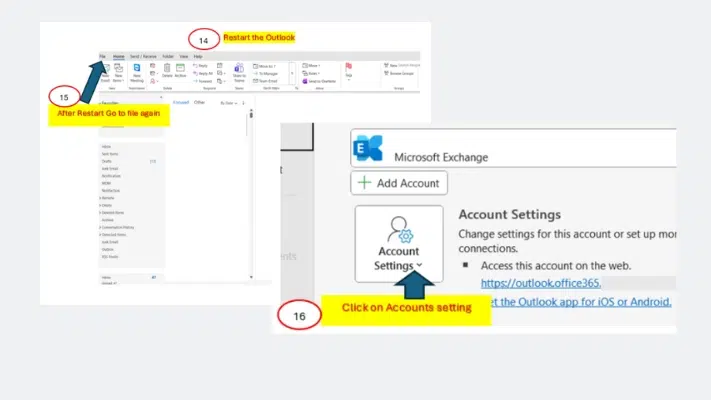
6. Restart Outlook Again

- After archiving is finished, restart Outlook one more time.
- After restart, go to File again.
- Click on Account Settings and then open Account Settings from the dropdown menu.
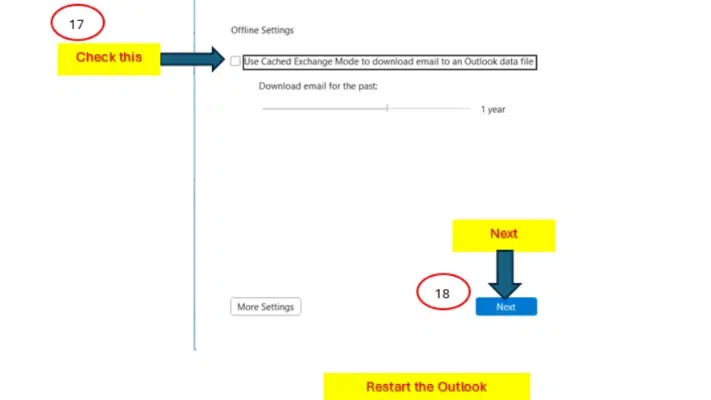
7. Re-enable Cached Exchange Mode

- In the Exchange Account Settings window, check the option “Use Cached Exchange Mode” again to re-enable it.
- Click Next, close the window, and then restart Outlook for the final time to apply the changes.
Best Practices for Outlook Mail Archiving
To maintain smooth Outlook performance, archive your emails every 3–6 months—or monthly if you receive large attachments. Keep multiple PST files organized with clear names and store them in a dedicated folder. Prevent corruption by keeping PST files under 10–12GB and backing them up regularly. For faster archiving, clean unwanted emails, disable extra add-ins, and run the process during low-usage hours.
How Often You Should Archive Your Emails
For most users, archiving emails every 3–6 months is ideal to maintain optimal Outlook performance. Heavy email users—especially those who receive large attachments—should archive monthly to prevent mailbox size from slowing down Outlook. Regular archiving ensures your active mailbox remains light, loads faster, and reduces the risk of hitting storage limits, particularly in corporate environments where mailbox quotas are enforced.
Organizing Multiple PST Files Efficiently
If you manage large volumes of email or multiple projects, you may end up with several PST archive files. To keep things organized, use clear, consistent naming conventions, such as “Archive-2023-H1.pst” or “Project-Alpha-Archive.pst.” Store PST files in a dedicated folder on your system or external drive to avoid confusion. Keep older PSTs read-only to prevent accidental editing, and avoid storing them on network drives, as this can cause performance issues or corruption.
Avoiding PST Corruption & Maintaining Backup
PST corruption commonly occurs due to improper shutdowns, oversized PST files, or storing them in unstable locations. To reduce risk, keep each PST file below 10–12 GB, as smaller files are more stable and easier to repair if needed. Always close Outlook properly before shutting down your PC. Maintain regular backups of your PST files—ideally on external storage or cloud sync—so you can restore your data if a file becomes corrupted. Running Microsoft’s Inbox Repair Tool (SCANPST) occasionally also helps maintain file health.
Tips for Faster Archiving
To speed up the archiving process, ensure Cached Exchange Mode is configured correctly and close any unnecessary Outlook add-ins. Archive emails during low-usage hours so Outlook can process files faster. Delete junk and unnecessary attachments beforehand—cleaner data means quicker archiving. Finally, keep your system SSD optimized, as PST writing is much faster on solid-state drives.
Troubleshooting Common Archive Issues
Archiving in Outlook is usually simple, but a few common issues can disrupt the process. If the Archive option is missing, enable AutoArchive or check account restrictions. When a PST file won’t open, repair it using SCANPST. If Outlook slows during archiving, close other apps and reduce archive size. For disk space errors, free storage or move the PST to another drive before restarting Outlook.
Archive Option Not Visible
If the Archive option doesn’t appear in your Outlook, it is usually due to disabled features or account type restrictions. Outlook connected to Microsoft 365 or Exchange accounts sometimes hides the Manual Archive option by default. To fix this, go to File → Options → Advanced and check if AutoArchive settings are enabled. If you are using an Exchange account, confirm with your IT admin whether archiving is allowed for your profile. Also, ensure Cached Exchange Mode is properly configured.
PST File Not Opening
A PST file may fail to open if it is corrupted, oversized, or stored in a restricted location. First, ensure the PST file is not blocked by Windows—right-click the file, go to Properties, and click Unblock if visible. If the issue persists, use Microsoft’s Inbox Repair Tool (SCANPST.exe) to fix the file. You should also confirm that the PST file is below Outlook’s recommended size limit (ideally under 10 GB) to avoid performance issues.
Outlook Becomes Slow During Archiving
Archiving emails can be resource-intensive, especially when processing large mailboxes. If Outlook slows down or freezes, close all other applications and allow the process to run uninterrupted. You can also reduce archive size by splitting archives into multiple PST files. Keeping your computer’s storage optimized and running periodic maintenance can improve archiving performance.
Not Enough Disk Space Error
This error occurs when your system doesn’t have sufficient free storage for the new PST file. Clear unnecessary files, delete temporary files, or move archives to an external drive. Check the storage path under Archive File Location and ensure the target drive has enough space. After cleaning up, restart Outlook and try again.
Alternatives to Manual Archiving
If you prefer a hands-off approach, Outlook offers several smart alternatives to manual archiving. AutoArchive automatically moves older emails to a separate PST file on a schedule you choose. Office 365’s Online Archive Mailbox stores old emails in the cloud, freeing local storage and improving performance. For advanced needs, third-party tools provide automated archiving, compliance support, and secure long-term email retention—ideal for businesses.
Using Auto Archive
Auto Archive is a built-in Outlook feature that automatically moves old emails to a separate archive file without requiring manual steps every time. You can set a schedule—daily, weekly, or monthly—and choose how old emails need to be before Outlook archives them. AutoArchive helps keep your mailbox lightweight, improves loading speed, and reduces the chances of Outlook freezing or slowing down. It’s ideal for users who regularly receive a high volume of emails and want maintenance to happen in the background with minimal effort.
Using Office 365 Online Archive Mailbox
For Office 365 users, the Online Archive Mailbox is one of the most powerful and convenient options. Instead of creating a local PST file, this feature stores older emails in the cloud, ensuring no storage burden on your computer. It offers huge mailbox capacity—often up to 100GB or more—and keeps your primary inbox clean. This is especially useful for corporate users who need to preserve emails for years without affecting Outlook performance.
Using Third-Party Archive Tools
Many organizations prefer third-party archiving tools for advanced features like automation, compliance, retention policies, and secure cloud backup. Tools such as Mail Store, GFI Archiver, or Barracuda offer centralized archiving, search capabilities, and audit trails. These solutions are ideal for businesses needing long-term storage, legal protection, and advanced email management beyond Outlook’s default options.
Conclusion
Why Regular Archiving Ensures Smooth Outlook Performance
Regular email archiving is essential for maintaining a fast, stable, and efficient Outlook experience. When your mailbox grows too large, Outlook can slow down, freeze, or take longer to search and sync data. By archiving older emails, you reduce mailbox load, improve responsiveness, and ensure that important messages are organized and easily accessible when needed. Archiving also protects your data by storing older emails in dedicated PST or cloud-based archive folders, preventing accidental loss and keeping your primary inbox clutter-free.
Final Tips for Long-Term Email Management
For long-term efficiency, set up a consistent archive routine—either manually or through features like AutoArchive or Office 365 Online Archive. Keep your PST files organized, back them up regularly, and avoid storing them on network drives to prevent corruption. Businesses looking for reliable, professional email management can rely on Chipin Corp, a trusted IT solutions provider in the UAE. Chipin offers expert support for email migration, Outlook optimization, data backup, and enterprise-level archiving solutions tailored to your workflow.
For assistance or professional email management services, you can visit:
🌐 Website: Chipin Corp
📩 Contact: +971 52 958 4840
Strong IT support and structured email management not only improve daily productivity but also enhance long-term data reliability—ensuring your Outlook runs smoothly at all times.